-
27-10-2017
A Novel Energy-efficient Cluster Formation Strategy_ from the Perspective of Cluster Members
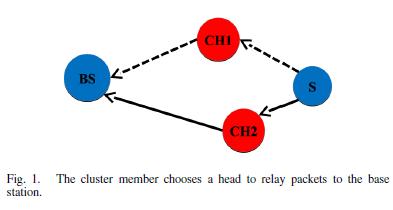
ABSTRACT Traditional clustering methods mostly concentrate on how to choose nodes to serve as cluster heads. As for cluster formation, most papers assume that a normal node joins a nearest cluster head. However, this is not an optimal solution to form a good cluster. It is shown in this paper that a cluster member may not response to the advertisement of the closest cluster head but join a farther cluster head in order to achieve better energy efficiency or longer co-alive lifespan. Based on our new observation, a novel cluster formation strategy is proposed. Besides, simulation results also verify the correctness of our analysis.[ Learn more ]
-
27-10-2017
A classification method for moving targets in the wild based on microphone array and linear sparse auto-encoder
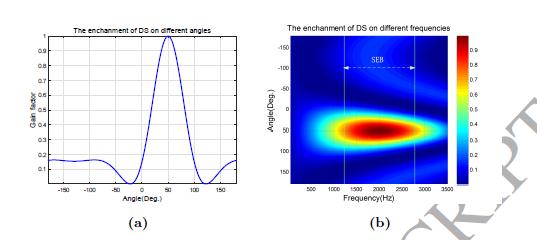
Moving target classification is an important issue in wireless sensors. The wild environment makes it a difficult problem for the acoustic signals. In this paper, a new classification method for moving targets in the wild is proposed based on microphone array and linear sparse auto-encoder (LSAE). Firstly, the acoustic signals of moving targets are enhanced by delay-and-sum (DS) beamformer in the narrawband way for the simplicity. [ Learn more ]
-
27-10-2017
A practical fundamental frequency extraction algorithm for motion parameters estimation of moving targets.
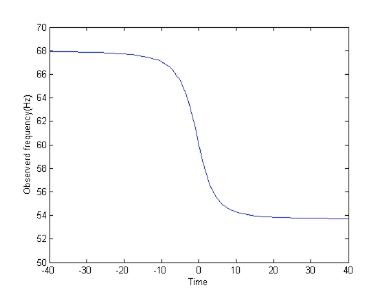
In this paper, a practical method is proposed for a moving target's fundamental frequency (MTFF) extraction from its acoustic signal. This method is developed for the application of motion parameters estimation. Starting from the analysis of the target frequency model and the acoustic Doppler model, the characteristics of moving target's signal are discussed. Based on the signatures of target's acoustic signal, a new approximate greatest common divisor (AGCD) method is developed to obtain an initial fundamental frequency (IFF). Then, the corresponding harmonic number associated with the IFF is determined by maximizing an objective function formulated as an impulse-train-weighted symmetric average magnitude sum function (SAMSF) of the obs...[ Learn more ]
-
09-06-2017
Intracluster Device-to-Device Relay Algorithm with Optimal Resource Utilization
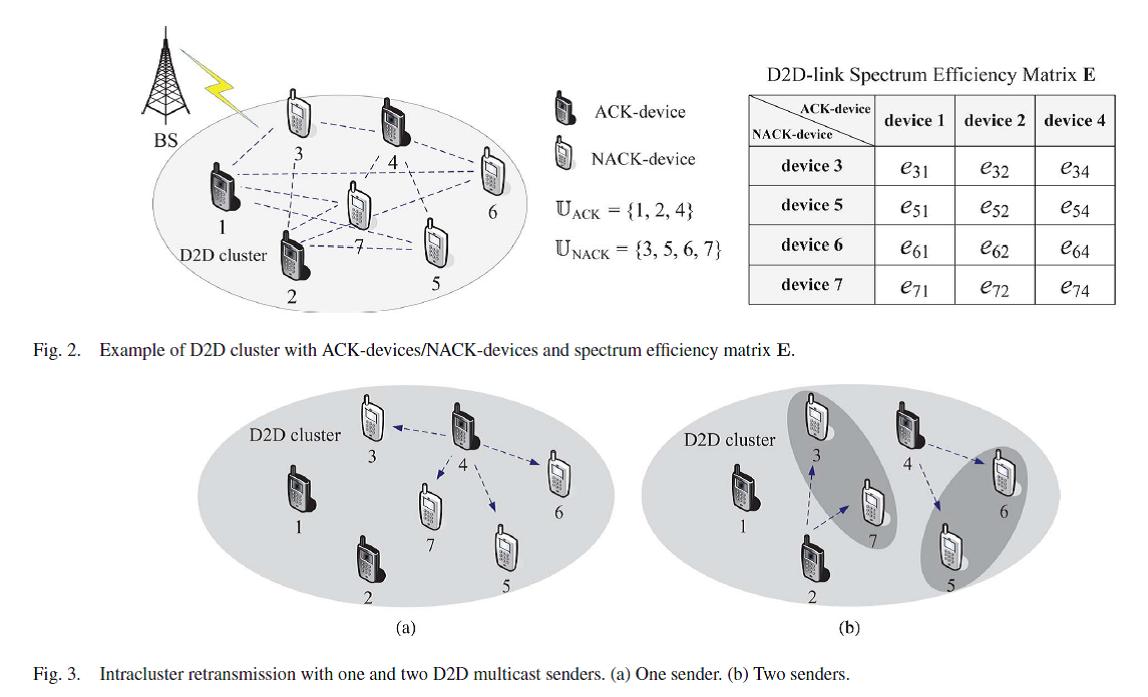
Device-to-device (D2D) communications help improve the performance of wireless multicast services in cellular networks via cooperative retransmissions among multicast recipients within a cluster. Resource utilization efficiency should be taken into account in the design of D2D communication systems. To maximize resource efficiency of D2D retransmissions, there is a tradeoff between multichannel diversity and multicast gain. In this paper, by analyzing the relationship between the number of relays and minimal time-frequency resource cost on retransmissions, we derive a closed-form probability density function (pdf) for an optimal number of D2D relays.Motivated by the analysis, we then propose an intracluster D2D retransmission scheme with...[ Learn more ]
-
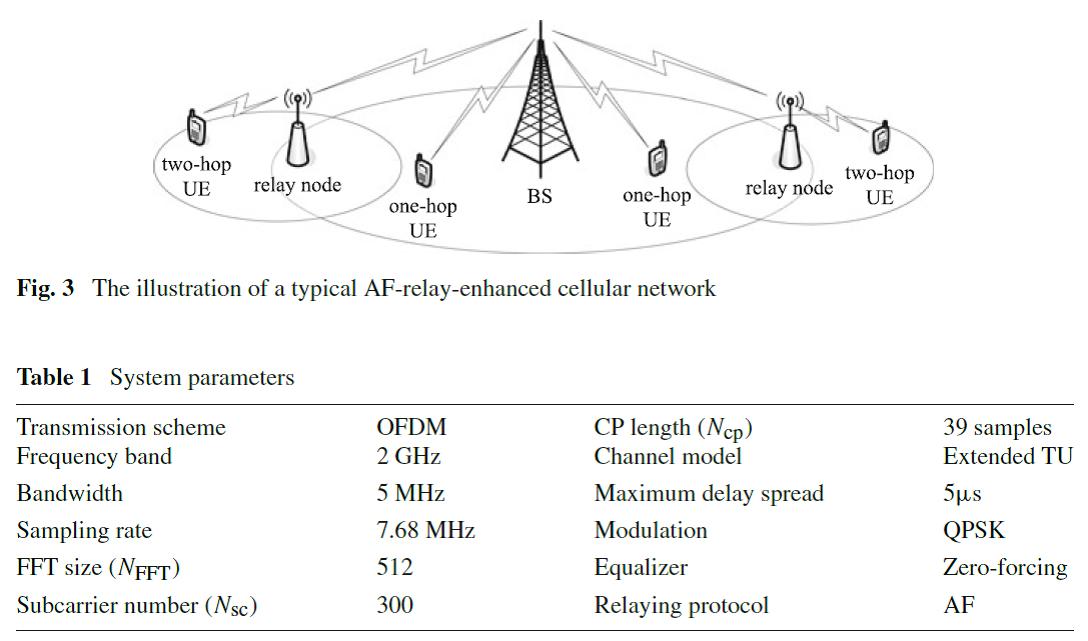
09-06-2017
Cyclic Prefix Update for OFDM Amplify-and-Forward Relay Systems
We consider half-duplex amplify-and-forward (AF) relaying for increasing network coverage and spectrum efficiency of an OFDM-based cellular system. Due to the fact that OFDM symbols are transmitted over two serial multipath channels (i.e., the source-relay link and the relay-destination link) via AF relaying, the time spread of the received signal at destination nodes is introduced by both source-relay and relay-destination channels. Consequently, cyclic prefix (CP) added at the source node should have a much longer length than that of one-hop OFDM transmission to avoid inter-symbol interference. [ Learn more ]